16
|
Culture Ways of Life and Wisdom
๏ Performing Arts
Performing Arts refer to the forms of arts including Lakorn
(drama), modern dance, traditional dance and music that coveys
stories. They can be formal or adapted from originals, performed
in front of audiences serving the purpose of beauty, entertainment,
thought-provoking which leads to social development and change.
The performances can be original or adapted, such as Lakorn, music
and local performance.
Performing Arts can be divided into 2 categories.
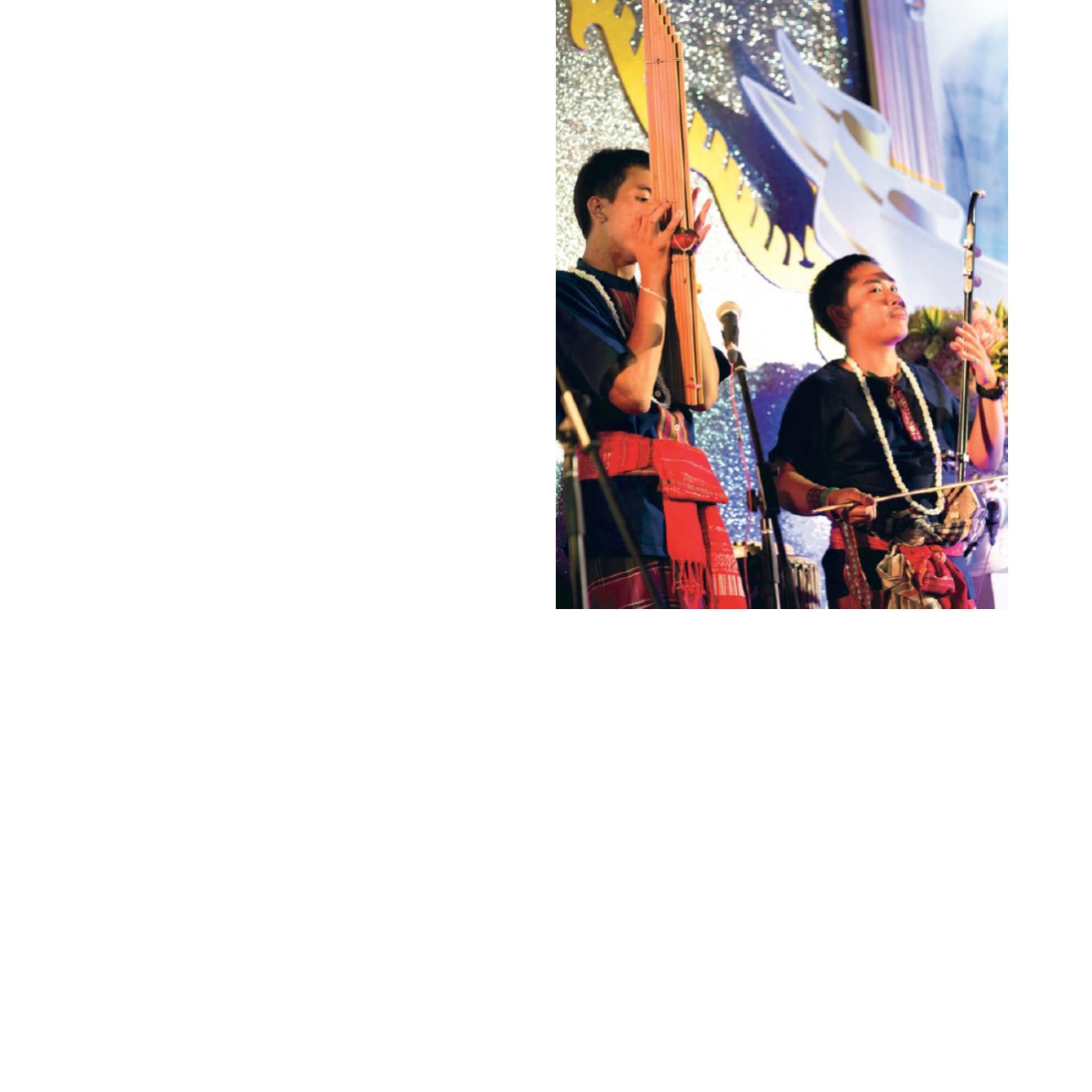
“Music and singing”
refers to the sound from musical
instrument and singing that composes music melodies, creating
pleasure or various moods. It also plays a role in driving moods,
providing entertainment, supporting acting or ritual performances.
As for the music, it can be classified as music for performances and
music for ritual performances such as playing Pin (stringed lute),
Can (reed mouth organ), wooden xylophone , flute, fiddle and singing
baby lullaby songs.
“Dramatic arts and Drama”
refer to a physical expression,
body movement, dance, use of voice, singing, use of scripts, use of
equipment, etc. to convey stories, moods and feelings, together with
or without music and singing. The performance is divided into ritual
performance, storytelling performance, and nonstory play, such as
Lakorn Nai, Li-kae, Khon. Mo Lam, Manohra, dance, etc.
๏ Social Practices, Rituals, Traditions and Festive Events
Social practices, rituals, traditions and festive events mean the
collective behaviors of people in the community that transmit through
generations and lead to the peaceful society and express the identity of
that community and ethnic group which can be devided as follows;
• Etiquette
means good behavior towards other people, such
as etiquette of speaking, paying respect, walking, sitting and squatting,
proper manners at the table, etc.
• Tradition
refers to continued behaviors and practices of
activities based on the lifestyle and society of the community such as religious
tradition, festive tradition, lifecycle tradition traditions about livelihood.
- Religion traditions e.g. Buddhist Holy Day, Buddhist Lent Day,
End of the Buddhist Lent Day, Visakha Bucha Day, Makha Bucha Day,
Asanha Bucha Day.
- Festive traditions e.g. Loy Krathong, Songkran, parades of
lent candles, Phi Ta Khon, the end of the tenth lunar month, Chak Phra
(Pulling the Buddha), Bun Pha Wet, Mahachati Sermon
- Lifecycle traditions from birth to death e.g. baby haircut,
tonsure, funeral ceremony, wedding ceremony, new house ceremony,
prolonging life tradition, ordination, requiem, traditional welcome ceremony
wrist-binding ceremony, Phuk Seui (Silk Festival for friendship)
- Traditions about livelihood e.g. Teacher veneration (Wai Khru)
ceremony, rice ritual (Kwan Khao), cat parade for rainfalls, Rocket Festival,
Royal Plowing Ceremony
• Culture and tradition of each Thai locality may differ by geography,
natural resources, environment, but remain their identity
of language, artefact, music, food and costume.